Every six weeks, we create a new branch of V8 as part of our release process. Each version is branched from V8’s Git master immediately before a Chrome Beta milestone. Today we’re pleased to announce our newest branch, V8 version 7.5, which is in beta until its release in coordination with Chrome 75 Stable in several weeks. V8 v7.5 is filled with all sorts of developer-facing goodies. This post provides a preview of some of the highlights in anticipation of the release.
WebAssembly #
Implicit caching #
We are planning to roll out implicit caching of WebAssembly compilation artifacts in Chrome 75. This means users that visit the same page a second time don’t need to compile the already-seen WebAssembly modules. Instead they are loaded from the cache. This works similarly to Chromium’s JavaScript code-cache.
In case you want to use a similar feature in your V8 embedding, please take inspiration from Chromium’s implementation.
Bulk memory operations #
The bulk memory proposal adds new instructions to WebAssembly for updating large regions of memory or tables.
memory.copy copies data from one region to another, even if the regions are overlapping (like C’s memmove). memory.fill fills a region with a given byte (like C’s memset). Similar to memory.copy, table.copy copies from one region of a table to another, even if the regions are overlapping.
(memory.copy (i32.const 0) (i32.const 1000) (i32.const 500))
(memory.fill (i32.const 100) (i32.const 123) (i32.const 1000))
(table.copy (i32.const 15) (i32.const 5) (i32.const 10))
The proposal also provides a way to copy a constant region into linear memory or a table. To do so, we first need to define a “passive” segment. Unlike “active” segments, these segments are not initialized during module instantiation. Instead they can be copied into a memory or table region using the memory.init and table.init instructions.
(data $hello passive "Hello WebAssembly")
(memory.init (i32.const 10) (i32.const 0) (i32.const 5))
(memory.init (i32.const 1000) (i32.const 6) (i32.const 11))
Numeric separators in JavaScript #
Large numeric literals are difficult for the human eye to parse quickly, especially when there are lots of repeating digits:
1000000000000
1019436871.42
To improve readability, a new JavaScript language feature enables underscores as separators in numeric literals. So, the above can now be rewritten to group the digits per thousand, for example:
1_000_000_000_000
1_019_436_871.42
Now it’s easier to tell that the first number is a trillion, and the second number is in the order of 1 billion.
For more examples and additional information about numeric separators, see our explainer.
Script streaming directly from network #
As of Chrome 75, V8 can stream scripts directly from network into the streaming parser, without waiting for the Chrome main thread.
While previous Chrome versions had streaming parsing and compilation, the script source data coming in from the network always had to make its way to the Chrome main thread first before being forwarded to the streamer, for historical reasons. This meant that often, the streaming parser would be waiting for data that has arrived from the network already, but hadn’t been forwarded to the streaming task yet because it was blocked by other things happening on the main thread (such as HTML parsing, layout, or other JavaScript execution).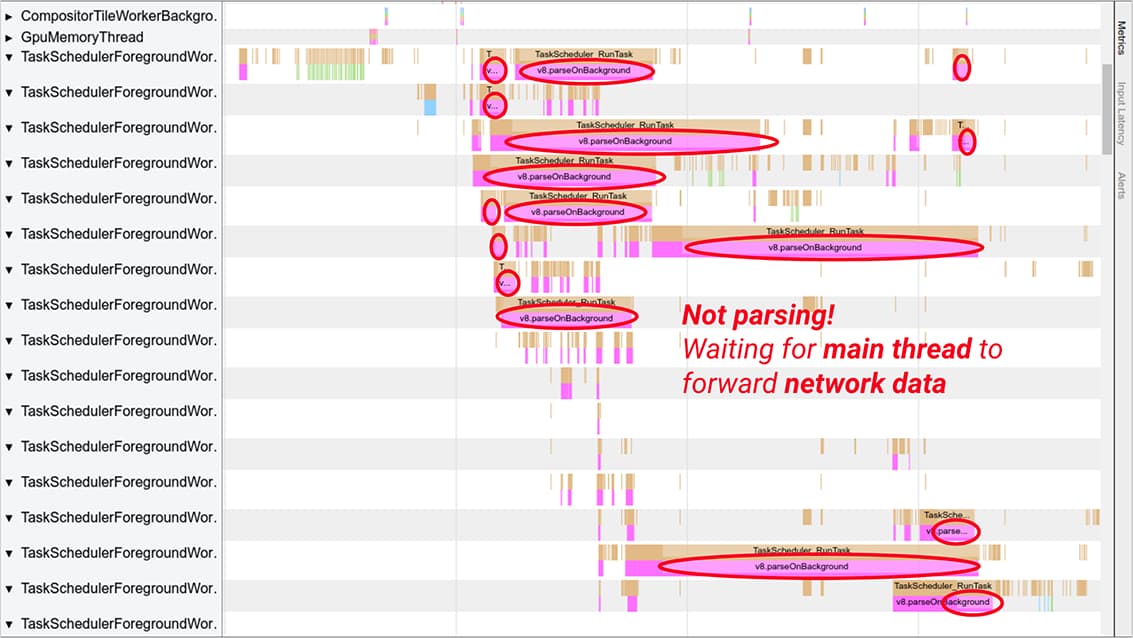 Stalled background parsing tasks in Chrome 74 and older
Stalled background parsing tasks in Chrome 74 and older
In Chrome 75, we connect the network “data pipe” directly to V8, allowing us to read network data directly during streaming parsing, skipping the dependency on the main thread.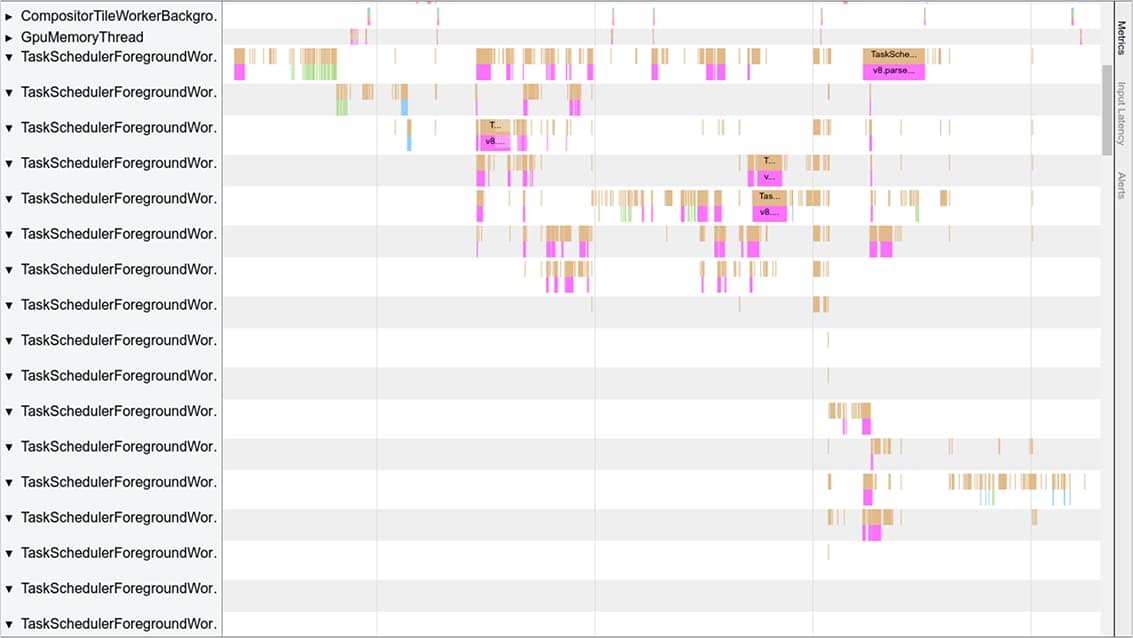 In Chrome 75+, background parsing tasks are no longer blocked by activity on the main thread.
In Chrome 75+, background parsing tasks are no longer blocked by activity on the main thread.
This allows us to finish streaming compiles earlier, improving the loading time of pages using streaming compilation, as well as reducing the number of concurrent (but stalled) streaming parse tasks, which reduces memory consumption.
V8 API #
Please use git log branch-heads/7.4..branch-heads/7.5 include/v8.h to get a list of the API changes.
Developers with an active V8 checkout can use git checkout -b 7.5 -t branch-heads/7.5 to experiment with the new features in V8 v7.5. Alternatively you can subscribe to Chrome’s Beta channel and try the new features out yourself soon.